Photogrammetry:
Where Art Meets Science in the World of Spatial Measurement
In today’s data-driven world, professionals across diverse industries rely on extracting valuable insights from images. Imagine a realm where photographs unlock hidden dimensions and precise measurements, empowering architects, engineers, and archaeologists. Welcome to the captivating world of photogrammetry, where art merges with science to analyze data! In this article, join us on an exhilarating journey as we explore the fundamental principles and techniques that drive this transformative process. Get ready to witness how photogrammetry empowers informed decision-making and reveals hidden insights.

‘Point cloud’ of the Three Graces by Antonio Canova © Factum Foundation
CONCEPT OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY
Photogrammetry is a remarkable technique that brings objects to life in three dimensions using photographs. It’s a perfect fusion of science and technology, enabling us to capture reliable information about the world by interpreting photographic images and radiant patterns. It’s both a science and an art, unlocking the magic of obtaining precise measurements through photography. With photogrammetry, the possibilities are endless. This versatile method of spatial measurement captures locations, lengths, shapes, sizes, areas, volumes, and more. It even allows us to understand variables like stress and velocity through spatial analysis over time. At its core, photogrammetry takes measurements from photographs, revealing precise metric information about an object. For example, architects can capture images of historic buildings and create accurate 3D models, enabling detailed analysis and renovation planning. Engineers can survey construction sites and generate topographic maps for infrastructure projects, while archaeologists document artifacts and archaeological sites, preserving cultural heritage through immersive 3D reconstructions.

Collecting bridge images for maintenance purposes
In practice, photogrammetry transforms photographs into gateways of discovery. It opens up a world of possibilities, ranging from intricate maps, and precise measurements, to breathtaking 3D models of real-world objects or scenes. Architects can turn static images into interactive fly-through visualizations, giving clients a realistic vision of their future projects. Engineers can simulate structures under different load conditions, optimizing designs for safety and efficiency. Archaeologists can digitally reconstruct ancient cities, allowing researchers and the public to explore long-lost civilizations from a fresh perspective.
Foundation of Photogrammetry
At the core of photogrammetry is the concept of triangulation, a fundamental geometric principle for determining the position of objects in space. By capturing multiple overlapping photographs from different angles, we create a rich source of visual information. This overlap allows us to identify common points in the images. By analyzing and measuring these shared points, we can determine the positions and orientations of the cameras used to capture the photos.
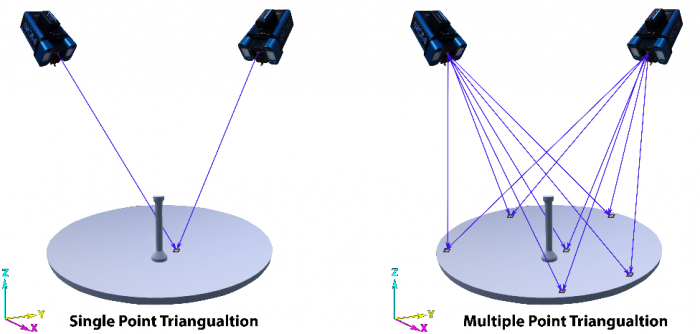
Single and multiple-point triangulation (Geodetic System)
Once we have the camera positions and orientations, we apply trigonometry, measuring angles and distances to calculate unknown values. In photogrammetry, we measure the angles formed by the lines of sight from the cameras to the points of interest. Incorporating known camera parameters and distances between cameras, we engage in triangulation. This process enables us to calculate the three-dimensional coordinates of the points, effectively reconstructing spatial information.

Point clouds are plotted in 3D space by using triangulation method (Virtuosity Blog)
In essence, photogrammetry relies on precise angle measurements, understanding camera parameters, and the careful analysis of overlapping photographs. These foundational principles empower us to extract three-dimensional details from two-dimensional images, providing a versatile and powerful method for capturing and comprehending the physical world.
DEVELOPMENT OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY
While this innovative field harnesses the power of photographs, its roots stretch back to the 15th century. Let’s delve into the captivating history of photogrammetry and explore its extraordinary development!

Info source from DARIAH and UBC
ADVANTAGES AND LIMITATIONS OF PHOTOGRAMMETRY
Photogrammetry, a technology that has stood the test of time and continues to evolve, offers numerous advantages across various domains. With its non-intrusive nature, cost-effectiveness, rapid processing capabilities, and adaptability to diverse industries, photogrammetry emerges as a powerful tool that unlocks a multitude of possibilities across numerous applications.:
- Seamless Data Collection: Photogrammetry enables non-intrusive remote data acquisition from aerial platforms like drones,
airplanes, or satellites. This approach is invaluable for gathering information from delicate or hard-to-reach areas and
ensuring personnel safety in high-risk environments. For example, in archaeology, photogrammetry preserves fragile artifacts
and historical sites without physical intervention. - Cost-Effectiveness: By using aerial platforms for data capture, such as drones or aircraft, photogrammetry brings cost
efficiencies. It efficiently covers large areas in a single flight or drone mission, reducing time and expenses compared to
ground-based methods. This scalability is advantageous for extensive mapping, surveying, or monitoring projects, minimizing
costs in architecture and urban planning. - Swift Data Acquisition and Processing: With high-resolution cameras and advanced software, photogrammetry facilitates
rapid data collection over expansive territories. It generates accurate 3D models and precise measurements by capturing
multiple images from different angles. Automated processing tools swiftly analyze large datasets, ensuring faster turnaround
times. Photogrammetry proves to be highly beneficial for forestry as it enables efficient forest inventory and monitoring,
making valuable contributions to sustainable management practices. - Versatility: Photogrammetry finds applications in diverse industries, accommodating small objects and large landscapes. It
offers customization options with different camera and sensor types, producing various data outputs such as orthophotos, 3D
models, and point clouds. Due to its versatility, photogrammetry plays a crucial role in engineering tasks, including
infrastructure assessment, monitoring, and maintenance, ensuring the integrity and safety of structures.
While exploring the advantages of photogrammetry, it’s important to acknowledge the limitations that come with it. However, these
limitations can be mitigated through specific strategies and approaches:
- Data Quality Dependency: The accuracy and reliability of photogrammetric data rely on the quality of the captured images.
Investing in higher-quality image-capturing equipment, conducting proper camera calibration, and optimizing lighting
conditions can enhance data quality. - Environmental Sensitivity: Factors like cloud cover, vegetation, and terrain variations can affect the accuracy of
photogrammetric measurements. Mitigation strategies include careful planning of data capture during optimal weather
conditions, applying advanced image processing techniques to handle vegetation and occlusions, and utilizing multi-sensor
integration for improved accuracy. - Vertical Measurement Accuracy: While photogrammetry excels in horizontal measurements, vertical measurements may
face limitations in dense urban areas or complex terrains. Employing accurate ground control points, aerial triangulation, and
integrating complementary techniques like LiDAR can enhance the vertical accuracy of photogrammetry. - Real-Time Data Projection: Photogrammetry typically involves post-processing steps, leading to a time delay between data
capture and the availability of final results. To minimize processing delays, advancements in hardware, such as high-speed
cameras and powerful processors, can be integrated with photogrammetric techniques for real-time or near-real-time
applications.
By understanding the capabilities and constraints of photogrammetry, professionals can harness its advantages while implementing strategies to mitigate limitations. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making and helps achieve optimal results across various applications.
FUTURE TRENDS
In conclusion, the future of photogrammetry is brimming with promise and endless possibilities. As technology advances and new innovations emerge, photogrammetry is set to become even more accessible, efficient, and versatile. The integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation will streamline data processing and analysis, delivering faster and more accurate results than ever before. Moreover, when combined with technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), photogrammetry offers immersive experiences and captivating visualizations that will push the boundaries of mapping, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. With every stride forward, photogrammetry will shape industries and revolutionize how we capture, analyze, and comprehend our world. So, as we look ahead, let’s embrace the exciting journey that lies ahead in the
captivating realm of photogrammetry!
